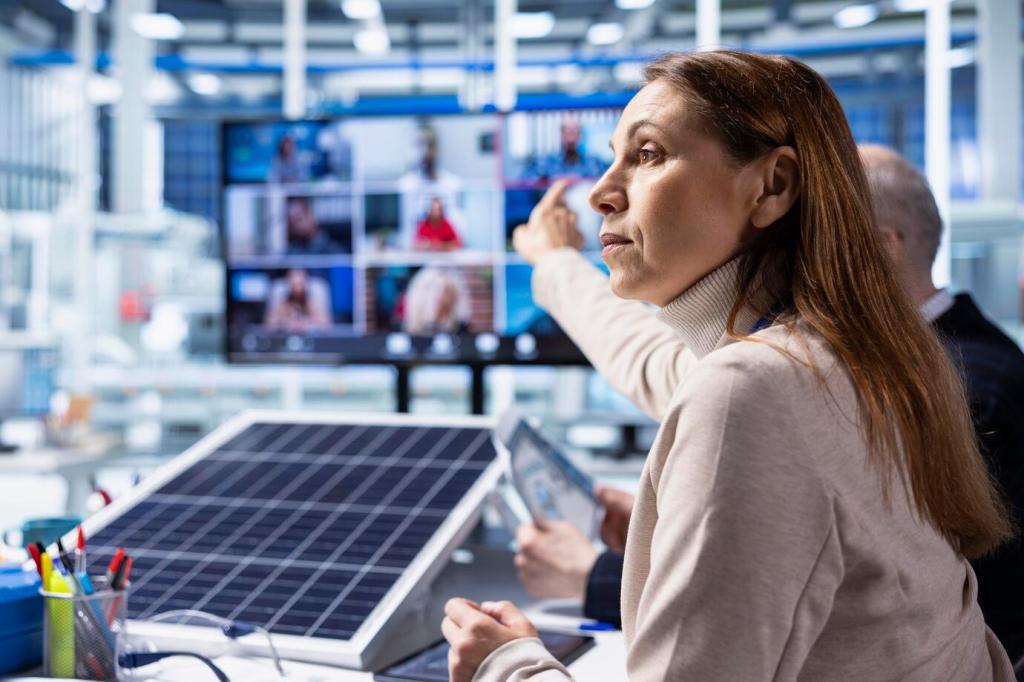
Standby Generators: Whole‑Home Guardians
Right‑sizing matters. Many homes thrive on 14–22 kW units, but real needs depend on HVAC tonnage, well pumps, medical devices, and startup surges. Share your must‑run appliances in the comments, and we’ll help you prioritize circuits for resilience without overspending.
Standby Generators: Whole‑Home Guardians
Natural gas offers plentiful, low‑maintenance runtime if your service is reliable; propane stores well on‑site for rural resilience; diesel shines in heavy‑duty applications with superior torque. Tell us your location and climate, and we’ll suggest the most robust option for your situation.